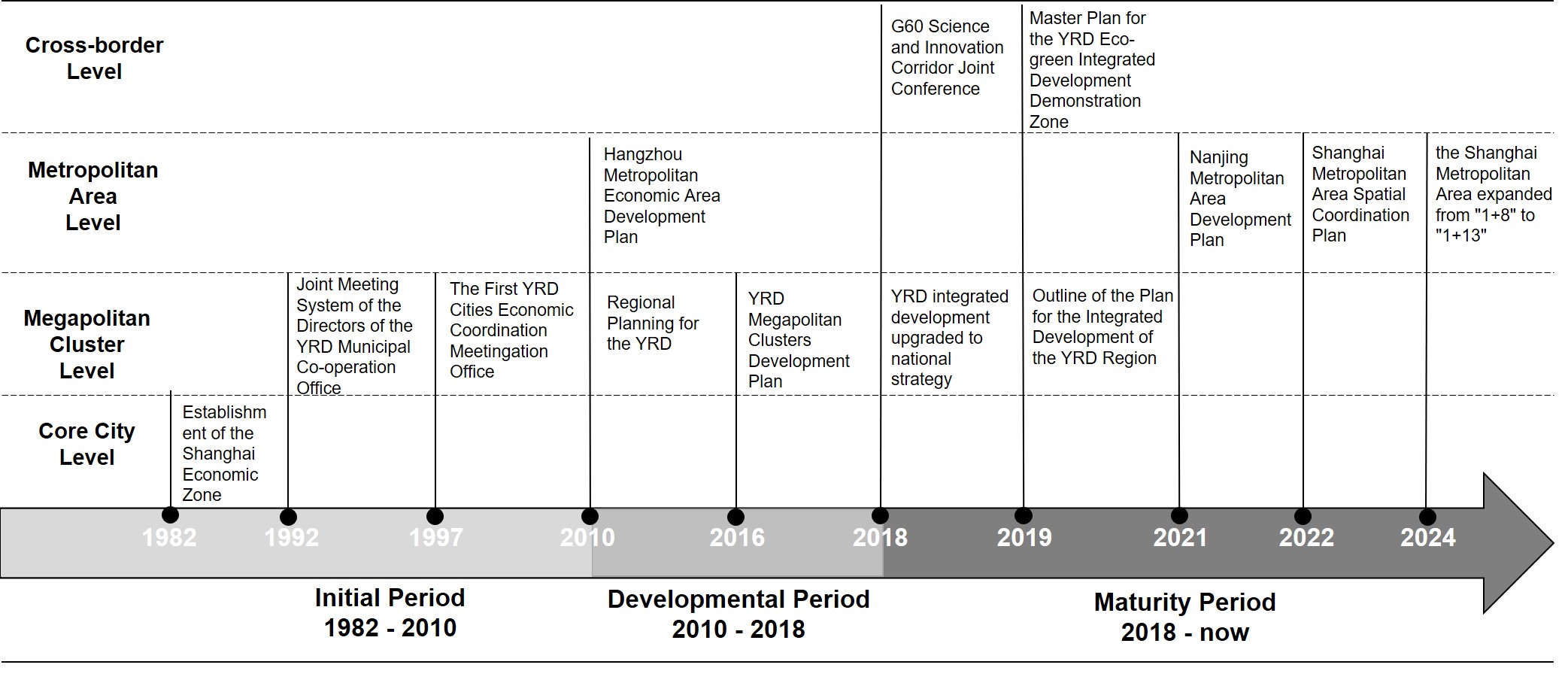
Development History: A Multi-Dimensional Region Centred on Shanghai
In the Chinese context, as urban spatial patterns and governance systems evolve, the concept of “region” increasingly exhibits multi-dimensional and dynamic characteristics, especially prominent in Shanghai and its surrounding areas. Shanghai is one of China’s four municipalities directly under the central government and a core city of the Yangtze River Delta (hereinafter referred to as YRD). The Shanghai Economic Zone was established in 1982, followed by the establishment of the YRD Joint Meeting System in 1992. In 2016, the State Council approved the “YRD Megapolitan Clusters (城市群) Development Plan,” and in 2018, the integrated development of the YRD was elevated to a national strategy.
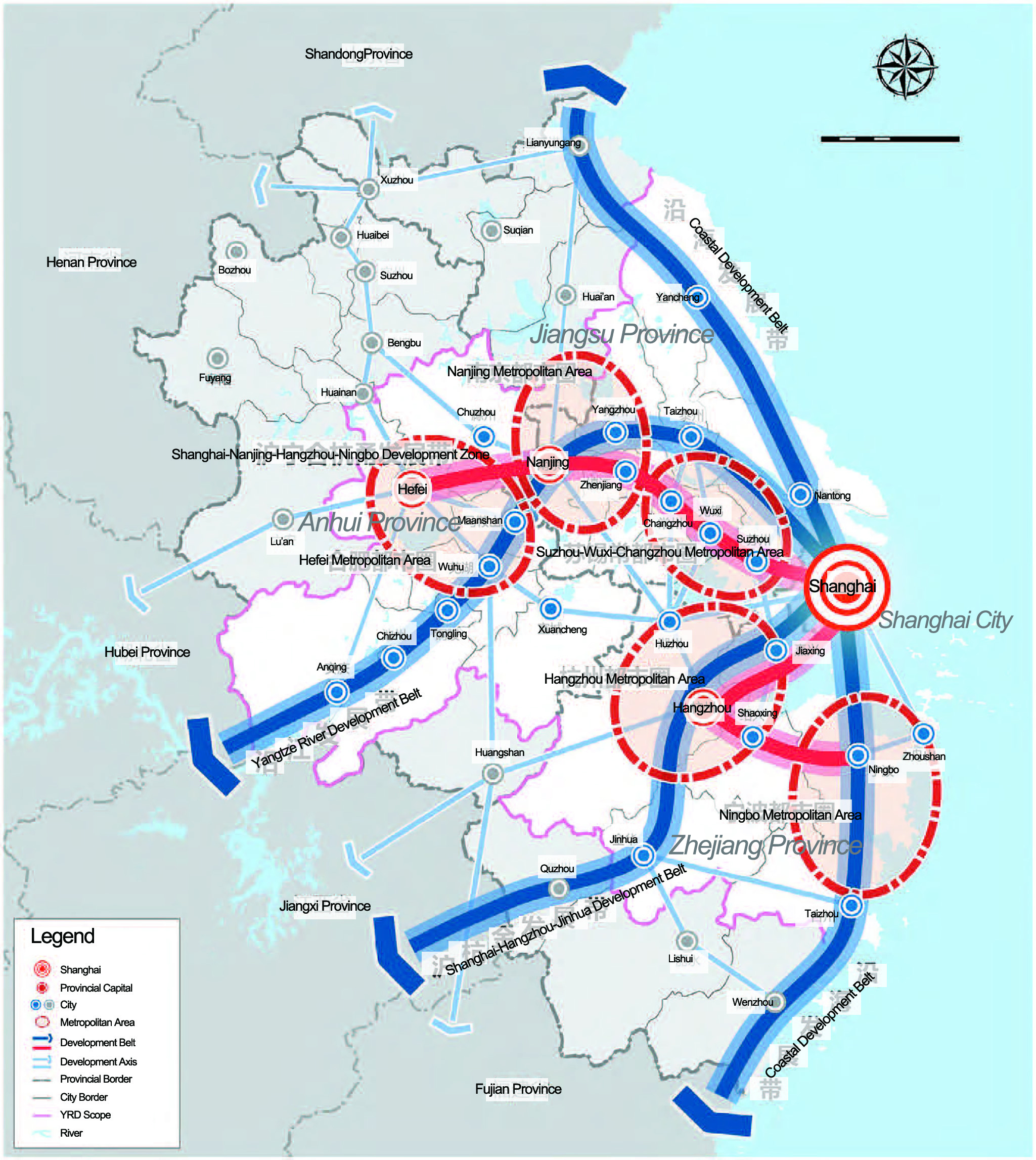
In its 2035 plan, Shanghai set the goal of building an “excellent global city” and aims to lead Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Anhui provinces in forming a world-class megapolitan cluster. Interactions between various cities have significantly increased, and these connections are continuously strengthened by the development of transportation networks and industrial layouts (Zhang, 2019). This further influences the urban network structure, sometimes even breaking through provincial boundaries and distance limitations. We aim to understand: What are the characteristics of mutual attention among city governments? In which fields do cities hope to establish connections with other cities? Are these connections influenced by proximities?
Linkage Measurement: Developmental Demands of Local Governments
In our study (Dou et al., 2025), we hypothesised that the number of frequencies (times) a city mentions another city in its planning text represents its level of attention to that city, and the specific sentence indicates the area of focus. We used the “14th Five-Year Plan” (FYP), a development strategy plan compiled by all cities every five years, from cities in the YRD as our research data. A total of 1,750 linkages were extracted from the texts of 41 cities across three provinces. Social network analysis (SNA) was employed to construct a linkage network model to quantify the strength of intergovernmental relationships, and the quadratic assignment procedure (QAP) was used to explore influencing factors. Simultaneously, textual statistical analysis was performed on the specific content of mutual mentions to investigate the main aspects covered by inter-city linkages.
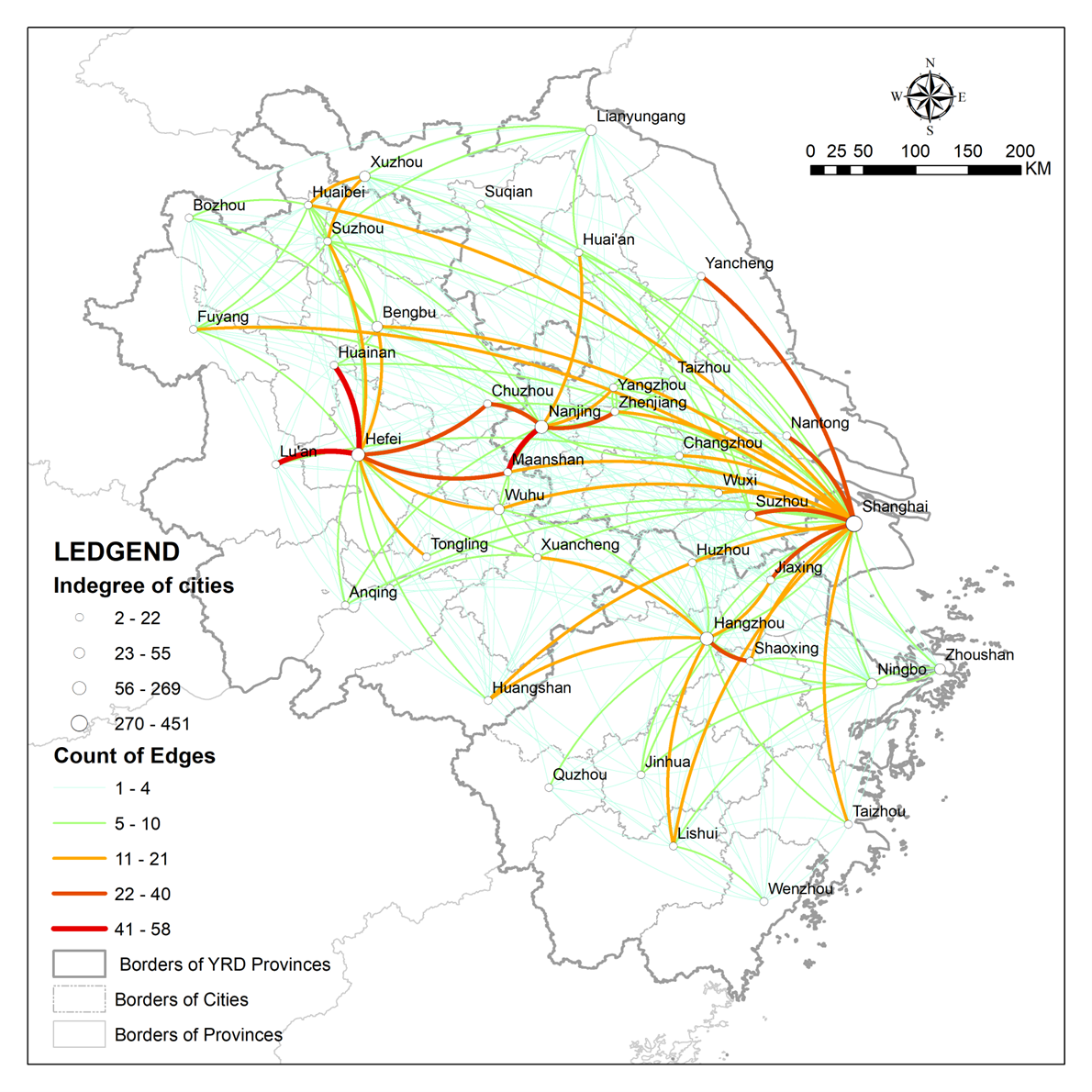
The research results indicate that the intergovernmental network in the YRD exhibits polarisation, with the top 8 cities accounting for 75.09% of all connections, as is visually represented by city icon sizes in Figure 3 (with line thickness and colour also indicating the strength and direction of inter-city connections). Cross-provincial connections (connections with cities outside their own province) account for half, and Shanghai has an attraction that covers the entire YRD. Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Anhui exhibit a progression from balanced to polarised network structures (with sequentially increasing Gini coefficients), and the cooperation areas of focus for cities in the three provinces are information technology, social culture, and infrastructure, respectively, verifying that the three provinces are at different stages of development.
We also note some exceptional cases: Lianyungang in northeastern Jiangsu and Zhoushan in eastern Zhejiang, despite ranking last in their respective provincial GDP rankings, both place third in indegree within their own provinces. Textual analysis reveals they receive significant attention due to their harbours and free trade zones. In contrast, Changzhou and Wuxi in southern Jiangsu exhibit relatively low indegree despite their top-tier provincial GDP rankings.
The QAP analysis results reveal the roles played by multidimensional proximities in network formation. Geographical proximity has a significant impact on intergovernmental networks, while the role of technological proximity (characterised by the number of patents granted) and information proximity (characterised by online search indices) is relatively weak, which may be related to inter-city competition.
Future Outlook: Application Value of the Research
By studying the 14th FYP texts of YRD cities, we analysed the development aspirations and demands of individual cities in the context of regional integration, providing a new perspective for regional-level planning evaluation and compilation, and providing insights for multi-scale spatial governance.
Cities in the YRD region have a strong willingness to connect. The network in the planning texts only partially reflects the willingness for inter-city connections. In reality, cities actively demonstrate their willingness to connect with other cities through diverse forms such as city agencies, paired assistance, and investment promotion conferences in other cities. New policy measures have also been introduced in recent years: in 2019, the State Council approved the YRD Eco-Green Integrated Development Demonstration Zone, in 2022, Shanghai City, Jiangsu Province, and Zhejiang Province jointly issued the “Shanghai Metropolitan Area Spatial Coordination Plan“, and in 2024, the Shanghai Metropolitan Area expanded from “1+8” to “1+13”. These initiatives signify that the YRD region has begun to explore more diversified cooperation models under the leadership of Shanghai, reducing obstacles to collaboration through institutional arrangements.
Based on our findings, we argue that to promote more balanced regional development, regional centre cities and their metropolitan areas should be formally clarified. This measure would not only enhance inter-city functional complementarity but also facilitate more specialised development orientations to prevent inefficient competition.
Connect with the Authors

Yin Dou is a PhD candidate at the College of Architecture and Urban Planning, Tongji University in Shanghai. His research focuses on big data-driven urban spatial analysis, intelligent planning methods, and transportation planning. He has been sponsored by the DAAD (German Academic Exchange Service) as a visiting scholar at the Technical University of Munich, Germany. He also serves as a member of the English website editorial committee of the Urban Planning Society of China.
![]() : Yin Dou
: Yin Dou ![]() : 0009-0009-5316-0730
: 0009-0009-5316-0730

Yishuai Zhang is an Assistant Professor at the School of Architecture and Urban Planning, Shenzhen University. His research focuses on multi-scalar urban structure analysis, regional governance, urban resilience and spatial intelligence simulation. He was selected as a High Impact Scholar (TOP 1%) of CNKI (Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure) in 2024.